|
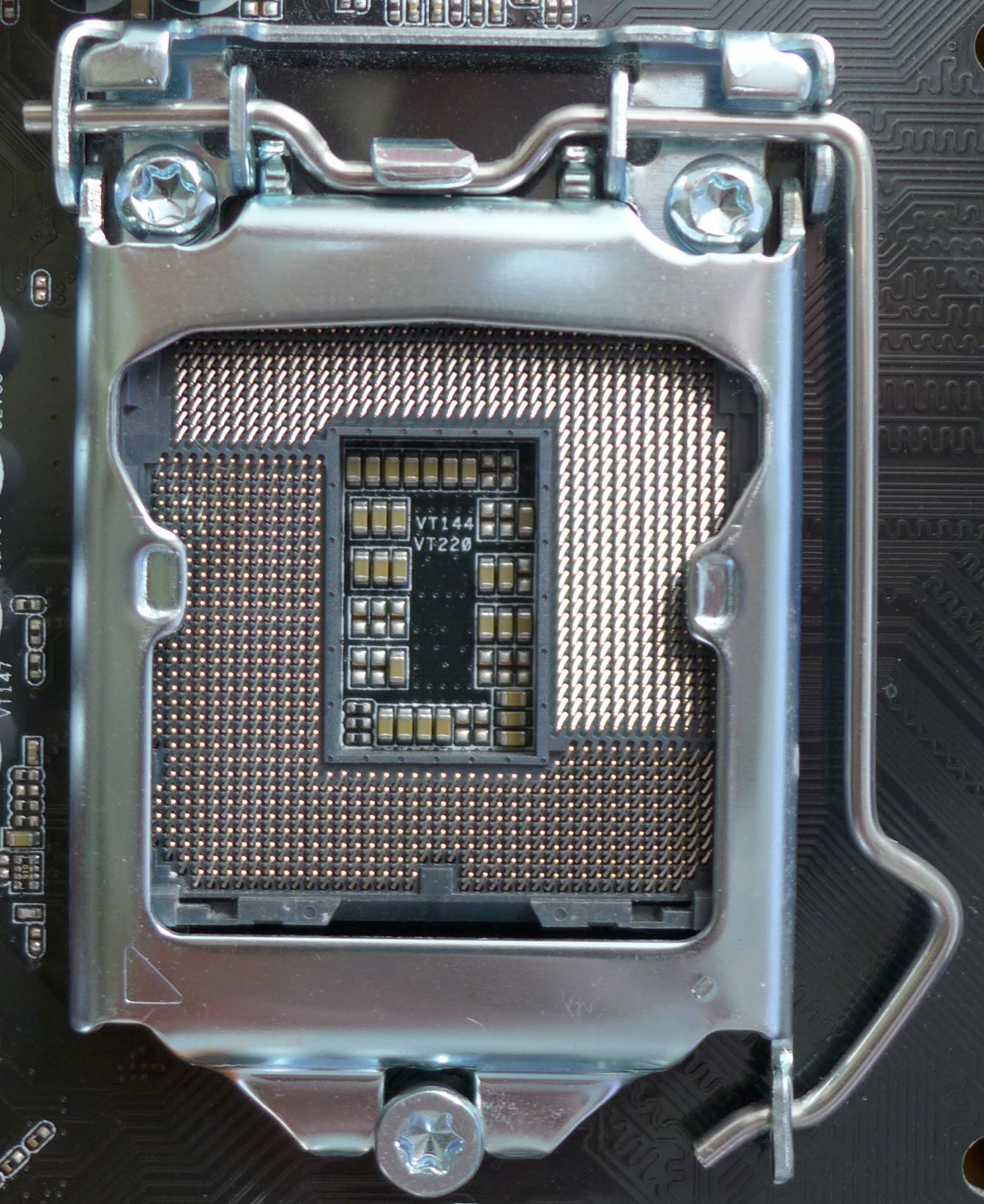
LGA 1151
LGA 1151, also known as Socket H4, is a type of zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket for Intel desktop processors which comes in two distinct versions: the first revision which supports both Intel's Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs, and the second revision which supports Coffee Lake CPUs exclusively. LGA 1151 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1150 (known as ''Socket H3''). LGA 1151 has 1151 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator, i.e. a voltage regulator which integrated on the CPU's die, introduced with Haswell and Broadwell, has again been moved to the motherboard. Most motherboards for the first revision of the socket support solely DDR4 memory, a lesser number support DDR3(L) memory, and the least number have slots for both DDR4 or DDR3(L) but only one memory type can be installed. Some have UniDIMM support, enabling either type of memory to be placed in the same DIMM, rather than h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 1151 Closed 01
Socket may refer to: Mechanics * Socket wrench, a type of wrench that uses separate, removable sockets to fit different sizes of nuts and bolts * Socket head screw, a screw (or bolt) with a cylindrical head containing a socket into which the hexagonal ends of an Allen wrench will fit * Socket termination, a termination used at the ends of wire rope#Sockets, wire rope * Socket, the receptacle into which a machine taper, tapered tool is inserted * Socket, an opening in any fitting that matches the outside diameter of a pipe or tube (fluid conveyance), tube Biology * Eye socket, a region in the skull where the eyes are positioned * Tooth socket, a cavity containing a tooth, in those bones that bear teeth * Dry socket, an opening as a result of the blood not clotting after a tooth is pulled * Ball and socket joint Computing * Network socket, an end-point in a communication across a network or the Internet * Unix domain socket, an end-point in local inter-process communication * socket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include pin grid array (PGA) or land grid array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard (called a ''planar device'' in the PCI specification) or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4K Resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) with a 16:9 aspect ratio is the dominant standard, whereas the digital cinema, movie projection industry uses 40962160 (Digital Cinema Initiatives, DCI 4K). The 4K television market share increased as prices fell dramatically throughout 2013 and 2014. 4K standards and terminology The term "4K" is generic and refers to any resolution with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000. Several different 4K resolutions have been standardized by various organizations. The terms "4K" and "Ultra HD" are used more widely in marketing than "2160p" (''cf.'' "1080p"). While typically referring to motion pictures, some digital camera vendors have used the term "4K photo" for still photographs, making it appear like an especially high resolution even though 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DisplayPort
DisplayPort (DP) is a digital interface used to connect a video source, such as a Personal computer, computer, to a display device like a Computer monitor, monitor. Developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), it can also carry digital audio, USB, and other types of data over a single cable. Introduced in the 2000s, DisplayPort was designed to replace older standards like VGA connector, VGA, DVI, and FPD-Link. While not directly compatible with these formats, Adapter, adapters are available for connecting to HDMI, DVI, VGA, and other interfaces. Unlike older interfaces, DisplayPort uses Data packet, packet-based transmission, similar to how data is sent over USB or Ethernet. The design enables support for high resolutions and adding new features without changing the connector. DisplayPort includes an auxiliary data channel used for device control and automatic configuration between source and display devices. It supports standards such as Display Data Channe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gaming consoles, and personal computers. HDMI supports uncompressed video and either compressed or uncompressed digital audio, allowing a single cable to carry both signals. Introduced in 2003, HDMI largely replaced older analog video standards such as composite video, S-Video, and VGA connector, VGA in consumer electronics. It was developed based on the CEA-861 standard, which was also used with the earlier Digital Visual Interface (DVI). HDMI is electrically compatible with DVI video signals, and adapters allow interoperability between the two without signal conversion or loss of quality. Adapters and active converters are also available for connecting HDMI to other video interfaces, including the older analog formats, as well as digital fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WiDi
Wireless Display (WiDi) is discontinued technology developed by Intel that enables users to stream music, movies, photos, videos and apps without cables from a compatible computer to a compatible HDTV or through the use of an adapter with other HDTVs or computer monitors. Intel WiDi supports HD 1080p video quality, 5.1 surround sound, and low latency for interacting with applications sent to the TV from a PC running Windows 7 or later. Using the Intel WiDi Widget, users can perform different functions simultaneously on their PC and TV such as checking email on the PC while streaming a movie to the TV from the same device. WiDi development was discontinued in 2016 in favor of Miracast, a standard developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance and natively supported by Windows 8.1 and later. Intel's Wireless Display should not be confused with Microsoft's Windows 11 operating system's built-in ''Wireless Display'' app (formerly ''Connect'') which works with Miracast. Version history * 2010 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Clear Video
Intel Clear Video is a semiconductor intellectual property core which implements some steps of some video decompression algorithms. The scope is to calculate these on the SIP core rather than on the CPU. Intel Clear Video is paired with integrated graphics processors branded as Intel GMA. Intel Clear Video HD is a set of post-processing features added to Intel Clear Video. See also * Intel Quick Sync Video – the successor of semiconductor intellectual property core to Intel Clear Video found on newer CPUs * Nvidia PureVideo * Unified Video Decoder Unified Video Decoder (UVD, previously called Universal Video Decoder) is the name given to AMD's dedicated video decoding ASIC. There are multiple versions implementing a multitude of video codecs, such as H.264 and VC-1. UVD was introduced wit ... (UVD) * Video Coding Engine (VCE) References External links Intel Clear Video Technologyarchived on Wayback Machine archived on Wayback Machine Clear Video Video acceleratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
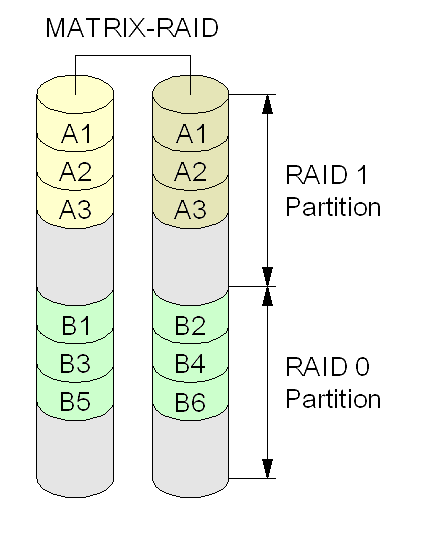
Intel Matrix RAID
Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a driver SATA AHCI and a firmware-based RAID solution built into a wide range of Intel chipsets. Currently also is installed as a driver for Intel Optane temporary storage units. It contains two operation modes that follow two Intel specific modes rather than the SATA standard. The name modes and the application that contains them have been renamed since the first version. Until 2010 it contains AHCI and Matrix RAID modes. The first mode is the Intel driver SATA normal and the latter mode is a fake RAID. Up to version 4 it is included on Intel Application Accelerator RAID Edition, between versions 5 and 8.9 it is included on Intel Matrix Storage Manager (IMSM), since version 9 it is included on Intel Rapid Storage Technology (IRST) preferring the driver modes to be named RST AHCI and RST AHCI RAID instead of Matrix RAID. The latter is also known as RST RAID mode, since it is the mode that Intel recommends to use, even if you are not work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VT-d
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU. In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities while attaining reasonable performance. In 2005 and 2006, both Intel ( VT-x) and AMD (AMD-V) introduced limited hardware virtualization support that allowed simpler virtualization software but offered very few speed benefits. Greater hardware support, which allowed substantial speed improvements, came with later processor models. Software-based virtualization The following discussion focuses only on virtualization of the x86 architecture protected mode. In protected mode the operating system kernel runs at a higher privilege such as ring 0, and applications at a lower privilege such as ring 3. In software-based virtualization, a host OS has direct access to hardware while the guest OSs have limited a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UniDIMM
UniDIMM (short for Universal DIMM) is a specification for dual in-line memory modules (DIMMs), which are printed circuit boards (PCBs) designed to carry dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) chips. UniDIMMs can be populated with either DDR3 or DDR4 chips, with no support for any additional memory control logic; as a result, the computer's memory controller must support both DDR3 and DDR4 memory standards. The UniDIMM specification was created by Intel for its Skylake microarchitecture, whose integrated memory controller (IMC) supports both DDR3 (more specifically, the DDR3L low-voltage variant) and DDR4 memory technologies. UniDIMM is a SO-DIMM form factor available in two dimensions: for the standard UniDIMM version (the same size as DDR4 SO-DIMMs), and for the low-profile version. UniDIMMs have a 260-pin edge connector, which has the same pin count as the one on DDR4 SO-DIMMs, with the keying notch in a position that prevents incompatible installation by making UniDIMMs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR3 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR and DDR2 and predecessor to DDR4 synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) chips. DDR3 SDRAM is neither forward nor backward compatible with any earlier type of random-access memory (RAM) because of different signaling voltages, timings, and other factors. DDR3 is a DRAM interface specification. The actual DRAM arrays that store the data are similar to earlier types, with similar performance. The primary benefit of DDR3 SDRAM over its immediate predecessor DDR2 SDRAM, is its ability to transfer data at twice the rate (eight times the speed of its internal memory arrays), enabling higher bandwidth or peak data rates. The DDR3 standard permits DRAM chip capacities of up to 8 gigabits (Gbit) (so 1 gigabyte by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |